Page 77 - Annual Report 2015 EN
P. 77
Annual Report 2015
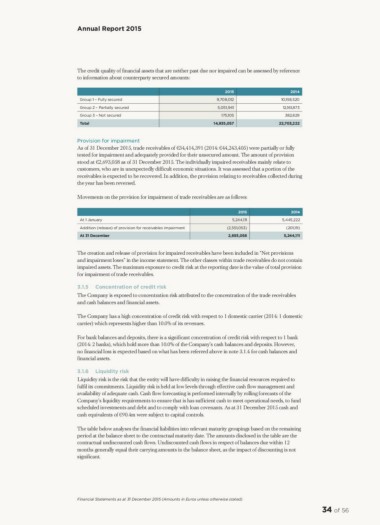
The credit quality of financial assets that are neither past due nor impaired can be assessed by reference
to information about counterparty secured amounts:
Group 1 – Fully secured 2015 2014
Group 2 – Partially secured 9,708,012 10,158,520
Group 3 – Not secured 5,051,941 12,161,873
Total
175,105 382,829
14,935,057 22,703,222
Provision for impairment
As of 31 December 2015, trade receivables of €34,414,391 (2014: €44,243,405) were partially or fully
tested for impairment and adequately provided for their unsecured amount. The amount of provision
stood at €2,693,058 as of 31 December 2015. The individually impaired receivables mainly relate to
customers, who are in unexpectedly difficult economic situations. It was assessed that a portion of the
receivables is expected to be recovered. In addition, the provision relating to receivables collected during
the year has been reversed.
Movements on the provision for impairment of trade receivables are as follows:
At 1 January 2015 2014
Addition (release) of provision for receivables impairment 5,244,111 5,445,222
At 31 December (2,551,053)
2,693,058 (201,111)
5,244,111
The creation and release of provision for impaired receivables have been included in “Net provisions
and impairment loses” in the income statement. The other classes within trade receivables do not contain
impaired assets. The maximum exposure to credit risk at the reporting date is the value of total provision
for impairment of trade receivables.
3.1.5 Concentration of credit risk
The Company is exposed to concentration risk attributed to the concentration of the trade receivables
and cash balances and financial assets.
The Company has a high concentration of credit risk with respect to 1 domestic carrier (2014: 1 domestic
carrier) which represents higher than 10.0% of its revenues.
For bank balances and deposits, there is a significant concentration of credit risk with respect to 1 bank
(2014: 2 banks), which hold more than 10.0% of the Company’s cash balances and deposits. However,
no financial loss is expected based on what has been referred above in note 3.1.4 for cash balances and
financial assets.
3.1.6 Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the entity will have difficulty in raising the financial resources required to
fulfil its commitments. Liquidity risk is held at low levels through effective cash flow management and
availability of adequate cash. Cash flow forecasting is performed internally by rolling forecasts of the
Company’s liquidity requirements to ensure that is has sufficient cash to meet operational needs, to fund
scheduled investments and debt and to comply with loan covenants. As at 31 December 2015 cash and
cash equivalents of €90.4m were subject to capital controls.
The table below analyses the financial liabilities into relevant maturity groupings based on the remaining
period at the balance sheet to the contractual maturity date. The amounts disclosed in the table are the
contractual undiscounted cash flows. Undiscounted cash flows in respect of balances due within 12
months generally equal their carrying amounts in the balance sheet, as the impact of discounting is not
significant.
Financial Statements as at 31 December 2015 (Amounts in Euros unless otherwise stated)
34 of 56
The credit quality of financial assets that are neither past due nor impaired can be assessed by reference
to information about counterparty secured amounts:
Group 1 – Fully secured 2015 2014
Group 2 – Partially secured 9,708,012 10,158,520
Group 3 – Not secured 5,051,941 12,161,873
Total
175,105 382,829
14,935,057 22,703,222
Provision for impairment
As of 31 December 2015, trade receivables of €34,414,391 (2014: €44,243,405) were partially or fully
tested for impairment and adequately provided for their unsecured amount. The amount of provision
stood at €2,693,058 as of 31 December 2015. The individually impaired receivables mainly relate to
customers, who are in unexpectedly difficult economic situations. It was assessed that a portion of the
receivables is expected to be recovered. In addition, the provision relating to receivables collected during
the year has been reversed.
Movements on the provision for impairment of trade receivables are as follows:
At 1 January 2015 2014
Addition (release) of provision for receivables impairment 5,244,111 5,445,222
At 31 December (2,551,053)
2,693,058 (201,111)
5,244,111
The creation and release of provision for impaired receivables have been included in “Net provisions
and impairment loses” in the income statement. The other classes within trade receivables do not contain
impaired assets. The maximum exposure to credit risk at the reporting date is the value of total provision
for impairment of trade receivables.
3.1.5 Concentration of credit risk
The Company is exposed to concentration risk attributed to the concentration of the trade receivables
and cash balances and financial assets.
The Company has a high concentration of credit risk with respect to 1 domestic carrier (2014: 1 domestic
carrier) which represents higher than 10.0% of its revenues.
For bank balances and deposits, there is a significant concentration of credit risk with respect to 1 bank
(2014: 2 banks), which hold more than 10.0% of the Company’s cash balances and deposits. However,
no financial loss is expected based on what has been referred above in note 3.1.4 for cash balances and
financial assets.
3.1.6 Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the entity will have difficulty in raising the financial resources required to
fulfil its commitments. Liquidity risk is held at low levels through effective cash flow management and
availability of adequate cash. Cash flow forecasting is performed internally by rolling forecasts of the
Company’s liquidity requirements to ensure that is has sufficient cash to meet operational needs, to fund
scheduled investments and debt and to comply with loan covenants. As at 31 December 2015 cash and
cash equivalents of €90.4m were subject to capital controls.
The table below analyses the financial liabilities into relevant maturity groupings based on the remaining
period at the balance sheet to the contractual maturity date. The amounts disclosed in the table are the
contractual undiscounted cash flows. Undiscounted cash flows in respect of balances due within 12
months generally equal their carrying amounts in the balance sheet, as the impact of discounting is not
significant.
Financial Statements as at 31 December 2015 (Amounts in Euros unless otherwise stated)
34 of 56